CCCP Lunar Program - Luna 24 Medals.
August 17, 2021
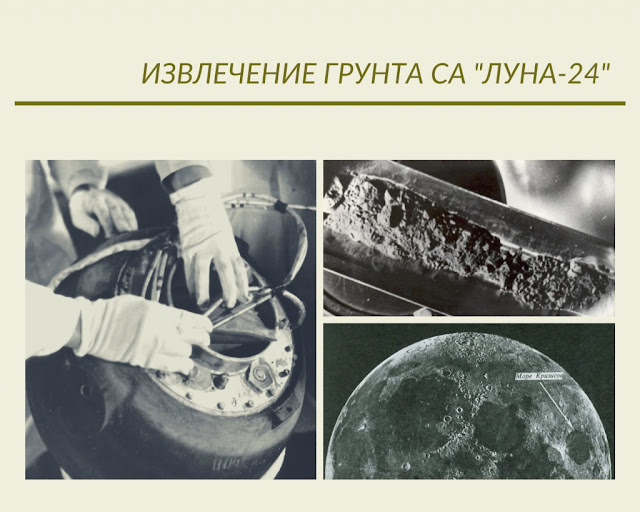
45 years ago, on August 18, 1976, the automatic interplanetary station "Luna-24" made a soft landing in the southeastern region of the Sea of Crises of a natural satellite of the Earth. After checking the state of the onboard systems and determining the position of the station on the lunar surface, a soil intake device was switched on by a command from the Earth.
Luna 24 station
The Sea of Crises is a 556 km2 basin, probably formed as a result of the fall of a massive cosmic body on the lunar surface 3-4 billion years ago. It is believed that its lava filling is one of the youngest on the Moon.
The automatic complex for the delivery of soil from the Moon "Luna-24" was created on the basis of the stations "Luna-16" and "Luna-20", but with some modifications. The main difference from its predecessors was the replacement of the soil intake device, due to which the soil entered and remained in the form of a column throughout the entire drilling process. In addition, the total drilling depth was 225 cm (the actual core length is 160 cm) - an order of magnitude deeper than the previous Luna-16 and Luna-20 vehicles.
After sampling the soil on August 19, the lander set off on a return rocket to the Earth and after 84 hours it separated to enter the dense layers of the atmosphere. The device landed in the estimated area 200 km from the city of Surgut. On this, his flight program was fully implemented. Now the mission's lander is in the museum of the S. A. Lavochkin Scientific and Production Association (part of the Roscosmos State Corporation).
The main result of the Luna-24 flight was the delivery of lunar soil samples to Earth. The delivered samples from regions of different structure completed a series of samples: the Sea of Plenty ("Luna-16"), its continental framing ("Luna-20") and the geological section of the Sea of Crises ("Luna-24").
In the soil column, 6 layers were distinguished by color, originating from the areas of distribution of dark basalt (volcanic) rocks. Soil analysis carried out on Earth showed the presence of about 60 elements with an increased content of aluminum and iron. In addition, it was assumed that the soil may contain water in a concentration of 0.1% by weight. Soil isotope analysis has made it possible to determine the age of lunar rocks from mountainous and marine areas and to better understand the geological history of the moon.
LROC view of Luna 24 on the Moon. Image Credit: NASA
Luna-24 was the last spacecraft of the Soviet program for exploring the Moon by interplanetary stations.
Related links:
ROSCOSMOS Press Release: https://www.roscosmos.ru/32213/
NPO Lavochkin: https://www.roscosmos.ru/tag/npo-lavochkina/
Roscosmos: https://www.roscosmos.ru/
Images, Text, Credits: ROSCOSMOS/Orbiter.ch Aerospace/Roland Berga.
Best regards, Orbiter.ch