ESO - European Southern Observatory logo.
May 12, 2022
First image of our black hole
Meet Sgr A*: Zooming into the black hole at the centre of our galaxy
The image is a long-anticipated look at the massive object that sits at the very centre of our galaxy. Scientists had previously seen stars orbiting around something invisible, compact, and very massive at the centre of the Milky Way. This strongly suggested that this object — known as Sagittarius A* (Sgr A*, pronounced "sadge-ay-star") — is a black hole, and today’s image provides the first direct visual evidence of it.
Making of the image of the black hole at the centre of the Milky Way
Size comparison of the two EHT black holes
Although we cannot see the black hole itself, because it is completely dark, glowing gas around it reveals a telltale signature: a dark central region (called a shadow) surrounded by a bright ring-like structure. The new view captures light bent by the powerful gravity of the black hole, which is four million times more massive than our Sun.
Image above: The Milky Way and the location of its central black hole as viewed from the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array.
European infrastructure involved in the EHT collaboration
Video montage of the Event Horizon Telescope observatories
“We were stunned by how well the size of the ring agreed with predictions from Einstein’s Theory of General Relativity," said EHT Project Scientist Geoffrey Bower from the Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Academia Sinica, Taipei. "These unprecedented observations have greatly improved our understanding of what happens at the very centre of our galaxy, and offer new insights on how these giant black holes interact with their surroundings." The EHT team's results are being published today in a special issue of The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
Side by side of the first two images of black holes
Comparison of the sizes of two black holes: M87* and Sagittarius A*
Because the black hole is about 27 000 light-years away from Earth, it appears to us to have about the same size in the sky as a doughnut on the Moon. To image it, the team created the powerful EHT, which linked together eight existing radio observatories across the planet to form a single “Earth-sized” virtual telescope [1]. The EHT observed Sgr A* on multiple nights in 2017, collecting data for many hours in a row, similar to using a long exposure time on a camera.
Montage of the Event Horizon Telescope observatories (day)
Montage of the Event Horizon Telescope observatories (night)
In addition to other facilities, the EHT network of radio observatories includes the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) and the Atacama Pathfinder EXperiment (APEX) in the Atacama Desert in Chile, co-owned and co-operated by ESO on behalf of its member states in Europe. Europe also contributes to the EHT observations with other radio observatories — the IRAM 30-meter telescope in Spain and, since 2018, the NOrthern Extended Millimeter Array (NOEMA) in France — as well as a supercomputer to combine EHT data hosted by the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy in Germany. Moreover, Europe contributed with funding to the EHT consortium project through grants by the European Research Council and by the Max Planck Society in Germany.
First image of our black hole (with wider background)
Locations of the telescopes that make up the EHT array
“It is very exciting for ESO to have been playing such an important role in unravelling the mysteries of black holes, and of Sgr A* in particular, over so many years,” commented ESO Director General Xavier Barcons. “ESO not only contributed to the EHT observations through the ALMA and APEX facilities but also enabled, with its other observatories in Chile, some of the previous breakthrough observations of the Galactic centre.” [2]
The EHT achievement follows the collaboration’s 2019 release of the first image of a black hole, called M87*, at the centre of the more distant Messier 87 galaxy.
The moon and the arc of the Milky Way
Size equivalent of the shadow of Sagittarius A*
The two black holes look remarkably similar, even though our galaxy’s black hole is more than a thousand times smaller and less massive than M87* [3]. "We have two completely different types of galaxies and two very different black hole masses, but close to the edge of these black holes they look amazingly similar,” says Sera Markoff, Co-Chair of the EHT Science Council and a professor of theoretical astrophysics at the University of Amsterdam, the Netherlands. "This tells us that General Relativity governs these objects up close, and any differences we see further away must be due to differences in the material that surrounds the black holes.”
ALMA and the centre of the Milky Way
APEX scratching the sky
This achievement was considerably more difficult than for M87*, even though Sgr A* is much closer to us. EHT scientist Chi-kwan (‘CK’) Chan, from Steward Observatory and Department of Astronomy and the Data Science Institute of the University of Arizona, USA, explains: “The gas in the vicinity of the black holes moves at the same speed — nearly as fast as light — around both Sgr A* and M87*. But where gas takes days to weeks to orbit the larger M87*, in the much smaller Sgr A* it completes an orbit in mere minutes. This means the brightness and pattern of the gas around Sgr A* were changing rapidly as the EHT Collaboration was observing it — a bit like trying to take a clear picture of a puppy quickly chasing its tail.”
APEX and snowy Chajnantor
Animation of the EHT network's radio telescopes
The researchers had to develop sophisticated new tools that accounted for the gas movement around Sgr A*. While M87* was an easier, steadier target, with nearly all images looking the same, that was not the case for Sgr A*. The image of the Sgr A* black hole is an average of the different images the team extracted, finally revealing the giant lurking at the centre of our galaxy for the first time.
Anatomy of a Black Hole
The effort was made possible through the ingenuity of more than 300 researchers from 80 institutes around the world that together make up the EHT Collaboration. In addition to developing complex tools to overcome the challenges of imaging Sgr A*, the team worked rigorously for five years, using supercomputers to combine and analyse their data, all while compiling an unprecedented library of simulated black holes to compare with the observations.
Wide-field view of the centre of the Milky Way
Artist's animation of the Milky Way
Scientists are particularly excited to finally have images of two black holes of very different sizes, which offers the opportunity to understand how they compare and contrast. They have also begun to use the new data to test theories and models of how gas behaves around supermassive black holes. This process is not yet fully understood but is thought to play a key role in shaping the formation and evolution of galaxies.
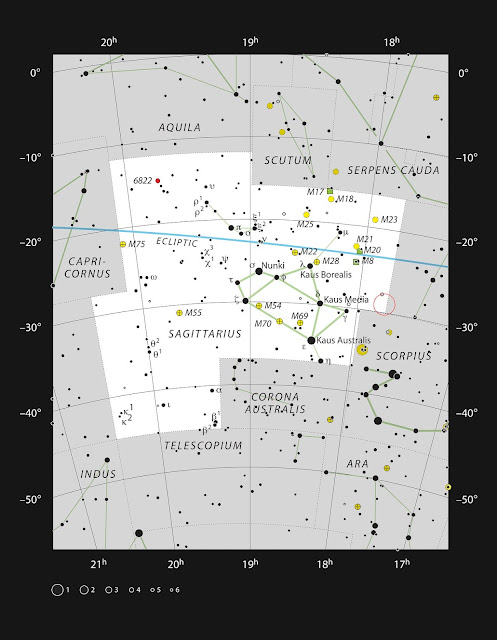
Sagittarius A* in the constellation of Sagittarius
“Now we can study the differences between these two supermassive black holes to gain valuable new clues about how this important process works,” said EHT scientist Keiichi Asada from the Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Academia Sinica, Taipei. “We have images for two black holes — one at the large end and one at the small end of supermassive black holes in the Universe — so we can go a lot further in testing how gravity behaves in these extreme environments than ever before.”
Clustering and averaging the images of Sagittarius A* and M87*
Progress on the EHT continues: a major observation campaign in March 2022 included more telescopes than ever before. The ongoing expansion of the EHT network and significant technological upgrades will allow scientists to share even more impressive images as well as movies of black holes in the near future.
Notes
[1] The individual telescopes involved in the EHT in April 2017, when the observations were conducted, were: the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), the Atacama Pathfinder EXperiment (APEX), the IRAM 30-meter Telescope, the James Clerk Maxwell Telescope (JCMT), the Large Millimeter Telescope Alfonso Serrano (LMT), the Submillimeter Array (SMA), the UArizona Submillimeter Telescope (SMT), the South Pole Telescope (SPT). Since then, the EHT has added the Greenland Telescope (GLT), the NOrthern Extended Millimeter Array (NOEMA) and the UArizona 12-meter Telescope on Kitt Peak to its network.
ALMA is a partnership of the European Southern Observatory (ESO; Europe, representing its member states), the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF), and the National Institutes of Natural Sciences (NINS) of Japan, together with the National Research Council (Canada), the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST; Taiwan), Academia Sinica Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics (ASIAA; Taiwan), and Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute (KASI; Republic of Korea), in cooperation with the Republic of Chile. The Joint ALMA Observatory is operated by ESO, the Associated Universities, Inc./National Radio Astronomy Observatory (AUI/NRAO) and the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ). APEX, a collaboration between the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy (Germany), the Onsala Space Observatory (Sweden) and ESO, is operated by ESO. The 30-meter Telescope is operated by IRAM (the IRAM Partner Organizations are MPG [Germany], CNRS [France] and IGN [Spain]). The JCMT is operated by the East Asian Observatory on behalf of The National Astronomical Observatory of Japan; ASIAA; KASI; the National Astronomical Research Institute of Thailand; the Center for Astronomical Mega-Science and organisations in the United Kingdom and Canada. The LMT is operated by INAOE and UMass, the SMA is operated by Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian and ASIAA and the UArizona SMT is operated by the University of Arizona. The SPT is operated by the University of Chicago with specialised EHT instrumentation provided by the University of Arizona.
The Greenland Telescope (GLT) is operated by ASIAA and the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory (SAO). The GLT is part of the ALMA-Taiwan project, and is supported in part by the Academia Sinica (AS) and MOST. NOEMA is operated by IRAM and the UArizona 12-meter telescope at Kitt Peak is operated by the University of Arizona.
[2] A strong basis for the interpretation of this new image was provided by previous research carried out on Sgr A*. Astronomers have known the bright, dense radio source at the centre of the Milky Way in the direction of the constellation Sagittarius since the 1970s. By measuring the orbits of several stars very close to our galactic centre over a period of 30 years, teams led by Reinhard Genzel (Director at the Max –Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics in Garching near Munich, Germany) and Andrea M. Ghez (Professor in the Department of Physics and Astronomy at the University of California, Los Angeles, USA) were able to conclude that the most likely explanation for an object of this mass and density is a supermassive black hole. ESO's facilities (including the Very Large Telescope and the Very Large Telescope Interferometer) and the Keck Observatory were used to carry out this research, which shared the 2020 Nobel Prize in Physics.
[3] Black holes are the only objects we know of where mass scales with size. A black hole a thousand times smaller than another is also a thousand times less massive.
More information
This research was presented in six papers published today in The Astrophysical Journal Letters:
https://iopscience.iop.org/journal/2041-8205/page/Focus_on_First_Sgr_A_Results
The EHT collaboration involves more than 300 researchers from Africa, Asia, Europe, North and South America. The international collaboration aims to capture the most detailed black hole images ever obtained by creating a virtual Earth-sized telescope. Supported by considerable international efforts, the EHT links existing telescopes using novel techniques — creating a fundamentally new instrument with the highest angular resolving power that has yet been achieved.
The EHT consortium consists of 13 stakeholder institutes; the Academia Sinica Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics, the University of Arizona, the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian, the University of Chicago, the East Asian Observatory, Goethe-Universitaet Frankfurt, Institut de Radioastronomie Millimétrique, Large Millimeter Telescope, Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy, MIT Haystack Observatory, National Astronomical Observatory of Japan, Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics, and Radboud University.
The Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), an international astronomy facility, is a partnership of ESO, the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) and the National Institutes of Natural Sciences (NINS) of Japan in cooperation with the Republic of Chile. ALMA is funded by ESO on behalf of its Member States, by NSF in cooperation with the National Research Council of Canada (NRC) and the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) and by NINS in cooperation with the Academia Sinica (AS) in Taiwan and the Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute (KASI). ALMA construction and operations are led by ESO on behalf of its Member States; by the National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO), managed by Associated Universities, Inc. (AUI), on behalf of North America; and by the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ) on behalf of East Asia. The Joint ALMA Observatory (JAO) provides the unified leadership and management of the construction, commissioning and operation of ALMA.
APEX, Atacama Pathfinder EXperiment, is a 12-metre diameter telescope, operating at millimetre and submillimetre wavelengths — between infrared light and radio waves. ESO operates APEX at one of the highest observatory sites on Earth, at an elevation of 5100 metres, high on the Chajnantor plateau in Chile’s Atacama region. The telescope is a collaboration between the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy (MPIfR), the Onsala Space Observatory (OSO), and ESO.
The European Southern Observatory (ESO) enables scientists worldwide to discover the secrets of the Universe for the benefit of all. We design, build and operate world-class observatories on the ground — which astronomers use to tackle exciting questions and spread the fascination of astronomy — and promote international collaboration in astronomy. Established as an intergovernmental organisation in 1962, today ESO is supported by 16 Member States (Austria, Belgium, the Czech Republic, Denmark, France, Finland, Germany, Ireland, Italy, the Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and the United Kingdom), along with the host state of Chile and with Australia as a Strategic Partner. ESO’s headquarters and its visitor centre and planetarium, the ESO Supernova, are located close to Munich in Germany, while the Chilean Atacama Desert, a marvellous place with unique conditions to observe the sky, hosts our telescopes. ESO operates three observing sites: La Silla, Paranal and Chajnantor. At Paranal, ESO operates the Very Large Telescope and its Very Large Telescope Interferometer, as well as two survey telescopes, VISTA working in the infrared and the visible-light VLT Survey Telescope. Also at Paranal ESO will host and operate the Cherenkov Telescope Array South, the world’s largest and most sensitive gamma-ray observatory. Together with international partners, ESO operates APEX and ALMA on Chajnantor, two facilities that observe the skies in the millimetre and submillimetre range. At Cerro Armazones, near Paranal, we are building “the world’s biggest eye on the sky” — ESO’s Extremely Large Telescope. From our offices in Santiago, Chile we support our operations in the country and engage with Chilean partners and society.
Links:
Related video:
What it Takes to Image a Black Hole
https://www.eso.org/public/videos/eso2208-eht-mwa/
Main papers:
Paper I: The Shadow of the Supermassive Black Hole in the Center of the Milky Way:
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/2041-8213/ac6674
Paper II: EHT and Multi-wavelength Observations, Data Processing, and Calibration:
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/2041-8213/ac6675
Paper III: Imaging of the Galactic Center Supermassive Black Hole:
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/2041-8213/ac6429
Paper IV: Variability, Morphology, and Black Hole Mass:
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/2041-8213/ac6736
Paper V: Testing Astrophysical Models of the Galactic Center Black Hole:
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/2041-8213/ac6672
Paper VI: Testing the Black Hole Metric:
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/2041-8213/ac6756
Supplementary papers:
Selective Dynamical Imaging of Interferometric Data:
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/2041-8213/ac6615
Millimeter Light Curves of Sagittarius A* Observed during the 2017 Event Horizon Telescope Campaign:
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/2041-8213/ac6428
A Universal Power Law Prescription for Variability from Synthetic Images of Black Hole Accretion Flows:
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/2041-8213/ac65eb
Characterizing and Mitigating Intraday Variability: Reconstructing Source Structure in Accreting Black Holes with mm-VLBI:
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/2041-8213/ac6584
ESO EHT web page: https://www.eso.org/public/science/event-horizon/
EHT Website & Press Release: https://eventhorizontelescope.org/
Images of ALMA: https://www.eso.org/public/images/archive/category/alma/
Images of APEX: https://www.eso.org/public/images/archive/category/apex/
ALMA: https://www.almaobservatory.org/en/home/
APEX: https://www.eso.org/public/teles-instr/apex/
30-meter Telescope operated by IRAM: http://www.iram-institute.org/EN/30-meter-telescope.php
JCMT: https://www.eaobservatory.org/jcmt/
LMT: http://www.lmtgtm.org/?lang=en
SMA: https://www.cfa.harvard.edu/sma/
SMT: http://aro.as.arizona.edu/
SPT: https://pole.uchicago.edu/
Greenland Telescope (GLT): https://lweb.cfa.harvard.edu/greenland12m/
NOEMA: https://www.iram-institute.org/EN/content-page-56-7-56-0-0-0.html
UArizona 12-meter telescope at Kitt Peak: https://aro.as.arizona.edu/?q=facilities/12m-telescope
ESO Very Large Telescope (VLT): https://www.eso.org/public/teles-instr/paranal-observatory/vlt/
ESO Very Large Telescope Interferometer (VLTI): https://www.eso.org/public/teles-instr/paranal-observatory/vlt/vlti/
Keck Observatory: https://www.keckobservatory.org/
Images Credits: EHT Collaboration/ESO/José Francisco Salgado (josefrancisco.org)/EHT collaboration (acknowledgment: Lia Medeiros, xkcd)/ESO/M. Kornmesser/ALMA/APEX/INAOE, LMT/N. Patel, GLT/EAO-W. Montgomerie, JCMT/D. Harvey, SMT/N. Billot, 30m/Wikipedia, SPT/S. R. Schimpf, SMA/IRAM, NOEMA/Wikipedia, Kitt Peak/N. Risinger (skysurvey.org)/ESO/L. Calçada/ESO/S. Guisard (www.eso.org/~sguisard)/ESO/B. Tafreshi (twanight.org)/ESO, C. Duran/ESO, Carlos A. Durán/ESO and Digitized Sky Survey 2. Acknowledgment: Davide De Martin and S. Guisard (www.eso.org/~sguisard)/ESO, IAU and Sky & Telescope/Videos Credits: ESO/L. Calçada, N. Risinger (skysurvey.org), DSS, VISTA, VVV Survey/D. Minniti DSS, Nogueras-Lara et al., Schoedel, NACO, GRAVITY Collaboration, EHT Collaboration (Music: Azul Cobalto)/ESO/M. Kornmesser, EHT Collaboration/ESO, ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO), IRAM/Diverticimes, NOEMA, F. Xavier Cuvelier, mediomix, Thalia Traianou (Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy) and B. Tafreshi (twanight.org)/ESO/L. Calçada/ESO/M. Kornmesser/L. Calçada/C. M. Fromm (University Würzburg, Germany), L. Rezzolla (University Frankfurt, Germany), EHT Collaboration/Text Credits: ESO, Bárbara Ferreira/EHT Project Director, JIVE and University of Leiden, Huib Jan van Langevelde/EHT Project Scientist, Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Academic Sinica, Taipei and University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa, US, Geoffrey Bower.
Best regards, Orbiter.ch







.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)