CERN - European Organization for Nuclear Research logo.
July 5, 2022
The collaboration has observed a new kind of “pentaquark” and the first-ever pair of “tetraquarks”
Image above: The new pentaquark, illustrated here as a pair of standard hadrons loosely bound in a molecule-like structure, is made up of a charm quark and a charm antiquark and an up, a down and a strange quark (Image: CERN).
The international LHCb collaboration at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) has observed three never-before-seen particles: a new kind of “pentaquark” and the first-ever pair of “tetraquarks”, which includes a new type of tetraquark. The findings, presented today at a CERN seminar, add three new exotic members to the growing list of new hadrons found at the LHC. They will help physicists better understand how quarks bind together into these composite particles.
Quarks are elementary particles and come in six flavours: up, down, charm, strange, top and bottom. They usually combine together in groups of twos and threes to form hadrons such as the protons and neutrons that make up atomic nuclei. More rarely, however, they can also combine into four-quark and five-quark particles, or “tetraquarks” and “pentaquarks”. These exotic hadrons were predicted by theorists at the same time as conventional hadrons, about six decades ago, but only relatively recently, in the past 20 years, have they been observed by LHCb and other experiments.
Large Hadron Collider (LHC) & CMS detector. Animation Credit: CERN
Most of the exotic hadrons discovered in the past two decades are tetraquarks or pentaquarks containing a charm quark and a charm antiquark, with the remaining two or three quarks being an up, down or strange quark or their antiquarks. But in the past two years, LHCb has discovered different kinds of exotic hadrons. Two years ago, the collaboration discovered a tetraquark made up of two charm quarks and two charm antiquarks, and two “open-charm” tetraquarks consisting of a charm antiquark, an up quark, a down quark and a strange antiquark. And last year it found the first-ever instance of a “double open-charm” tetraquark with two charm quarks and an up and a down antiquark. Open charm means that the particle contains a charm quark without an equivalent antiquark.
The discoveries announced today by the LHCb collaboration include new kinds of exotic hadrons. The first kind, observed in an analysis of “decays” of negatively charged B mesons, is a pentaquark made up of a charm quark and a charm antiquark and an up, a down and a strange quark. It is the first pentaquark found to contain a strange quark. The finding has a whopping statistical significance of 15 standard deviations, far beyond the 5 standard deviations that are required to claim the observation of a particle in particle physics.
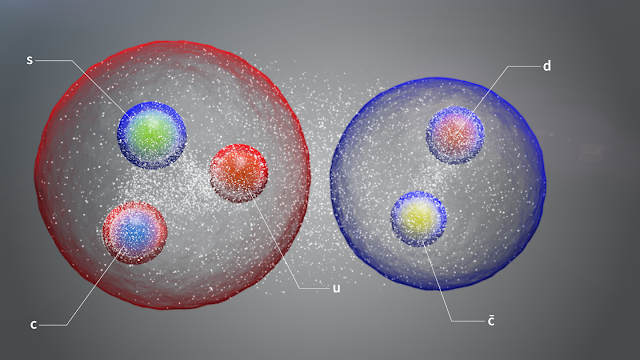
Image above: The two new tetraquarks, illustrated here as single units of tightly bound quarks. One of the particles is composed of a charm quark, a strange antiquark and an up quark and a down antiquark (left), and the other is made up of a charm quark, a strange antiquark and an up antiquark and down quark (right) (Image: CERN).
The second kind is a doubly electrically charged tetraquark. It is an open-charm tetraquark composed of a charm quark, a strange antiquark, and an up quark and a down antiquark, and it was spotted together with its neutral counterpart in a joint analysis of decays of positively charged and neutral B mesons. The new tetraquarks, observed with a statistical significance of 6.5 (doubly charged particle) and 8 (neutral particle) standard deviations, represent the first time a pair of tetraquarks has been observed.
“The more analyses we perform, the more kinds of exotic hadrons we find,” says LHCb physics coordinator Niels Tuning. “We’re witnessing a period of discovery similar to the 1950s, when a ‘particle zoo’ of hadrons started being discovered and ultimately led to the quark model of conventional hadrons in the 1960s. We’re creating ‘particle zoo 2.0’.”
“Finding new kinds of tetraquarks and pentaquarks and measuring their properties will help theorists develop a unified model of exotic hadrons, the exact nature of which is largely unknown,” says LHCb spokesperson Chris Parkes. “It will also help to better understand conventional hadrons.”
While some theoretical models describe exotic hadrons as single units of tightly bound quarks, other models envisage them as pairs of standard hadrons loosely bound in a molecule-like structure. Only time and more studies of exotic hadrons will tell if these particles are one, the other or both.
Note:
CERN, the European Organization for Nuclear Research, is one of the world’s largest and most respected centres for scientific research. Its business is fundamental physics, finding out what the Universe is made of and how it works. At CERN, the world’s largest and most complex scientific instruments are used to study the basic constituents of matter — the fundamental particles. By studying what happens when these particles collide, physicists learn about the laws of Nature.
The instruments used at CERN are particle accelerators and detectors. Accelerators boost beams of particles to high energies before they are made to collide with each other or with stationary targets. Detectors observe and record the results of these collisions.
Founded in 1954, the CERN Laboratory sits astride the Franco–Swiss border near Geneva. It was one of Europe’s first joint ventures and now has 23 Member States.
Related links:
Large Hadron Collider (LHC): https://home.cern/science/accelerators/large-hadron-collider
LHCb: https://home.cern/science/experiments/lhcb
List of new hadrons found at the LHC: https://www.nikhef.nl/~pkoppenb/particles.html
For more information about European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN), Visit: https://home.cern/
Images (mentioned), Animation (mentioned), Text, Credits: CERN/LHCb collaboration.
Greetings, Orbiter.ch



-labels_0.png)